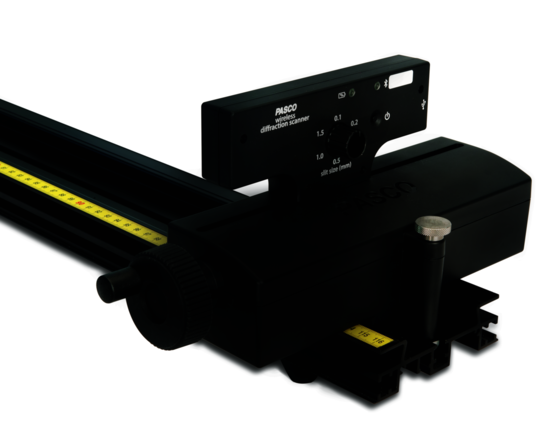
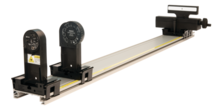
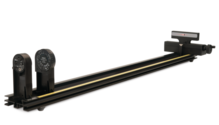
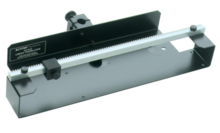
The Wireless Diffraction Scanner combines a position sensor with a light sensor for scanning diffraction patterns.
- 1x USB Charging Cable
See the Buying Guide for this item's required, recommended, and additional accessories.
Product Summary
The Wireless Diffraction Scanner combines a position sensor with a light sensor for scanning diffraction patterns. Compatible with PASCO optics benches (or dynamics track adapter carriages), the Wireless Diffraction Scanner is the perfect update to existing PASCO-based optics systems that use the snap-in optics components. An included aperture setting allows for the adjustment of width-measurement resolution (and light attenuation). A hand crank allows for smooth scanning of diffraction patterns. Because of the wireless design, smooth scans are achieved effortlessly!
This unit enables students to scan many diffraction and interference patterns during one lab period. They can study the differences caused by changing the slit width, slit separation, and number of slits. And, by comparing patterns created by a Red Diode Laser to those of a Green Diode Laser, they can study the difference caused by a change in wavelength.
Measurement control is achieved using either PASCO Capstone or SPARKvue software (required). Connect to software using either USB or Bluetooth Low Energy.
The all-in-one design of the Wireless Diffraction Scanner makes setup simple and fast! Quickly adjust light level with the included aperture dial to achieve perfect diffraction pattern scans.
Features
- Compatible with PASCO-based optics systems
- Adjustable aperture
- Connects using USB or Bluetooth Low Energy
- Rechargeable Battery
- Controllable with PASCO Capstone or SPARKvue Software
How It Works
The wireless Diffraction Scanner combines an optical position encoder with a light sensor in a carriage system that can be moved using a scanner adjustment wheel. When a diffracted laser beam is aligned with the aperture opening, the resulting pattern can be scanned by turning the adjustment wheel and measuring the light intensity at every position with the internal light sensor. The aperture dial on the carriage can be used to attenuate the light incident on the light sensor. This adjusts the width of the aperture slit (0.1 mm - 1.5 mm). This also determines the spatial width that the light sensor can resolve.
What's Included
- 1x USB Charging Cable
Product Specifications
| Aperture Range | 0.1 mm to 1.5 mm |
| Position Resolution | .01 mm |
| Scan Travel | 155 mm |
| Connectivity | USB or Bluetooth® Low Energy |
| Battery Type | Rechargeable LiPo (1000 mA) |
Data Collection Software
This product requires PASCO software for data collection and analysis. We recommend the following option(s). For more information on which is right for your classroom, see our Software Comparison: SPARKvue vs. Capstone »
Connectivity Options
This product can connect directly to your computer or device with the following technologies. No Interface required. See the following guide for details regarding device compatibility: Wireless Bluetooth Product Compatibility »
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Buying Guide
| Recommended Accessories | P/N | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Green Diode Laser | OS-8458B | -- |
| Red Diode Laser | OS-8525A | -- |
| Optics Track, 1.2 m | OS-8508 | -- |
| Diffraction Slits | OS-8442 | -- |
| Replacement Parts | P/N | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Micro USB Cable | PS-3584 | -- |
Experiment Library
Perform the following experiments and more with the Wireless Diffraction Scanner.
Visit PASCO's Experiment Library to view more activities.
Interference from a Double Slit
The purpose of this experiment is to examine the diffraction and interference patterns formed by laser light passing through two slits and verify that the positions of the maxima in the interference pattern match the positions...
Diffraction from a Single Slit
The purpose of this experiment is to examine the diffraction pattern formed by laser light passing through a single slit and verify that the positions of the minima in the diffraction pattern match the positions predicted by theory.
Interference of Different Wavelengths
The purpose of this experiment is to examine the diffraction and interference patterns formed by laser light of two different wavelengths passing through two slits. The wavelength of each laser beam will be determined using the...
Interference and Diffraction - Wireless
Interference and diffraction patterns from laser light passing through various single-slits and multiple-slits are scanned and plotted in real time. These patterns are then examined for similarities and differences.
Interference from Multiple Slits
The purpose of this experiment is to examine the diffraction and interference pattern formed by laser light passing through multiple slits, observing how the number of slits is related to the maxima intensity and peak width.
Support Documents
| Manuals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wireless Diffraction Scanner Manual | English - 331.71 KB | |
| Safety Sheets | ||
| Lithium Battery Safety Data Sheet | English - 593.55 KB | |
| Knowledge Base | ||
| How do I troubleshoot connecting a wireless sensor? | Aug 22nd, 2022 | |
| Wireless sensor or device not charging | Mar 4th, 2024 | |
| Battery replacement instructions for OS-8441 | Aug 7th, 2023 | |
| Battery warranty for rechargeable lithium ion and lithium polymer batteries | Mar 13th, 2023 | |
| Devices not shown properly in SPARKvue or PASCO Capstone | Apr 14th, 2022 | |
| How to install the Data Streamer app extension within Microsoft Excel | Apr 5th, 2023 | |