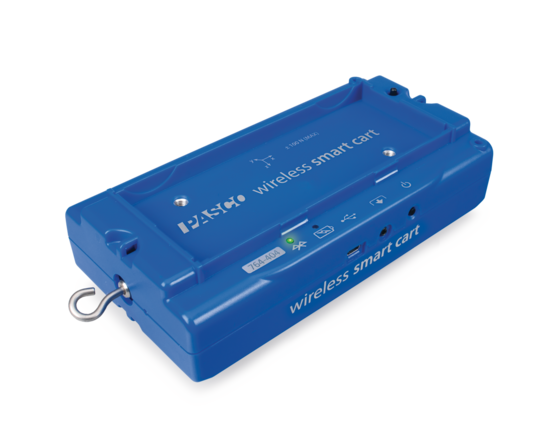


The Smart Cart is the ultimate tool for your physics lab with built-in sensors that measure force, position, velocity, three axes of acceleration, and three axes of rotational velocity. U.S. Patent No. 10,481,173
- 1x Hook
- 1x Rubber bumper
- 1x Magnetic bumper
- 1x USB cable for charging
See the Buying Guide for this item's required, recommended, and additional accessories.
Product Summary
The patented Smart Cart is the ultimate tool for studying kinematics, dynamics, Newton’s Laws, and more. It is based on a durable ABS body with nearly frictionless wheels, just like our high quality PAScars. Now, we’ve added built-in sensors that measure force, position, velocity, and acceleration. The versatile Smart Cart can collect measurements on or off a track and transmit the data wirelessly over Bluetooth. In essence, it is a wireless dynamics cart that combines all the necessary sensors, without requiring any additional hardware.
Smart Carts are ideal for studying mechanics topics, such as kinematics and dynamics. The built-in load cells enable two Smart Carts to visually demonstrate Newton’s Third Law with ease. Additionally, built-in sensors for force and acceleration enable students to investigate Newton’s Second Law in minutes. Smart Carts truly are a physics lab on wheels, and now you can own the most advanced physics cart ever created, all without the restrictions of cables.
 |
 |
 |
Features
- Built-in ±100N force sensor
- 3-axis accelerometer
- 3-axis rotational velocity sensor
- A Built-in wheel encoder
- Bluetooth® connectivity
- Rechargeable battery
- Magnetic bumper for force sensor
- 3-position plunger
- Mass tray
- Velcro® tabs
- Force sensor hook and rubber bumper
Applications
- Kinematics
- Acceleration on an incline (determining g)
- Newton’s Laws
- Impulse
- Conservation of Momentum
- Elastic & Inelastic Collisions
- Conservation of Energy
- Simple Harmonic Oscillators (using the spring set)
- Magnetic damping (using the Magnetic Damping Bumper)
- And much more!
What's Included
- 1x Hook
- 1x Rubber bumper
- 1x Magnetic bumper
- 1x USB cable for charging
Product Specifications
| Optical Encoder |
|
| Accelerometer |
|
| Force Sensor |
|
| Gyro Sensor |
|
| Mass Without Accessories | 250 g |
| Patent No. | 10481173 |
| Connectivity | USB and Bluetooth 5.2 |
| Logging | No |
| Battery Type | Rechargeable LiPo |
Battery & Logging
| Stored Data Points Memory (Logging) 1 | Not Supported |
| Battery - Connected (Data Collection Mode) 2 | Up to 7 hr |
| Battery - Logging (Data Logging Mode) 3 | Not Supported |
| Battery Type | LiPo |
1 Minimum # of data points with all measurements enabled, actual results depend on enabled measurements.
2 Continuous use in a connected state until battery failure, actual results will depend on sample rate, active measurements, and battery condition.
3 Logging until battery failure, actual results will depend on sample rate, active measurements, and battery condition.
* Normal classroom use is the sensor in active use for 20min/lab for 120 lab periods/yr.
Data Collection Software
This product requires PASCO software for data collection and analysis. We recommend the following option(s). For more information on which is right for your classroom, see our Software Comparison: SPARKvue vs. Capstone »
Connectivity Options
This product can connect directly to your computer or device with the following technologies. No Interface required. See the following guide for details regarding device compatibility: Wireless Bluetooth Product Compatibility »
Dedicated Datalogging with SPARK LXi2
Consider an all-in-one, touchscreen data collection, graphing, and analysis tool for students. Designed for use with wired and wireless sensors, the SPARK LXi2 Datalogger simultaneously accommodates up to five wireless sensors and includes two ports for blue PASPORT sensors. It features an interactive, icon-based user interface within a shock-absorbing case and arrives packaged with SPARKvue, MatchGraph!, and Spectrometry software for interactive data collection and analysis. It can additionally connect via Bluetooth to the following interfaces: AirLink, SPARKlink Air, and 550 Universal Interface.
Buying Guide
| Recommended Accessories | P/N | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Cart Mass (Set of 2) | ME-6757A | -- |
| Smart Fan Accessory | ME-1242 | -- |
| Smart Cart Rod Stand Adapter | ME-1244 | -- |
| Smart Cart Charging Garage | ME-1243 | -- |
| Bumper Accessory Set | ME-9884 | -- |
| Smart Cart Motor | ME-1247 | -- |
| Replacement Parts | P/N | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Bumper Set | ME-9885A | -- |
| Micro USB Cable | PS-3584 | -- |
| Also Available | P/N | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Cart (Red) | ME-1240 | -- |
| Dynamics Cart Magnetic Damping | ME-6828 | -- |
| USB Bluetooth Adapter | PS-3500 | -- |
| Standard Metal Cart Metal Track 1.2 m System | ME-5715A | -- |
Product Guides & Articles
Dynamics Cart & Track System Configuration
Dynamics Systems provide an engaging and affordable method for physics educators to teach a variety of complex concepts in Kinematics and Dynamics. We offer a wide range of carts and tracks that make it easy to design your ideal Dynamics System, while staying under budget. In addition to durable equipment, PASCO Dynamics Systems also include access to a wealth of downloadable lab acitivities designed to get students hands-on and experimenting with key physics concepts.
Smart Cart to Vernier Comparison
The Smart Cart may appear to be equivalent to competitors like Vernier’s Go Direct Sensor Cart–they include many of the same features and specifications–but several distinctions set the PASCO Smart Cart apart.
Experiment Library
Perform the following experiments and more with the Smart Cart (Blue).
Visit PASCO's Experiment Library to view more activities.
Periodic Motion: Mass and Spring
Experimentally determine the physical properties of a hanging mass and spring system that affect its period of oscillation.
Newton's Second Law
The acceleration of a Smart Cart with Smart Fan Accessory is measured for varying forces, while keeping the mass constant. The Smart Fan is used to produce a thrust, and the Smart Cart’s sensors are used to measure both the...
Archimedes’ Principle
In this lab, the buoyant force on an object is measured by taking the difference between the object's weight in air, and its apparent weight in water. This measured buoyant force is compared to the theoretical value calculated...
Coefficients of Friction
Experimentally determine the static and kinetic friction coefficients between two contacting surfaces.
External Force and Newton's Laws
The external force exerted by the hand through the elastic band causes the system of two carts to accelerate. The carts’ sensors are used to measure the forces and the acceleration. Theoretical values of the acceleration and...
Average Speed and Velocity
Use a Smart Cart to graph position versus time. Use the data to compare average speed and velocity to instantaneous velocity.
Newton's First Law
The purpose of this experiment is to determine how external forces influence the motion of a Smart Cart, either by itself, or together with a Friction Block, or tied by a string to masses hanging over a pulley. Analysis of this...
Conservation of Energy
How does the mechanical energy of a cart change as its motion changes due to gravity? Perform an experiment that explores how a cart's kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, and total mechanical energy change as it rolls...
Conservation of Momentum
Students use two Smart Carts and a dynamics system to demonstrate that linear momentum and kinetic energy are conserved in an elastic collision, and linear momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not conserved in an inelastic...
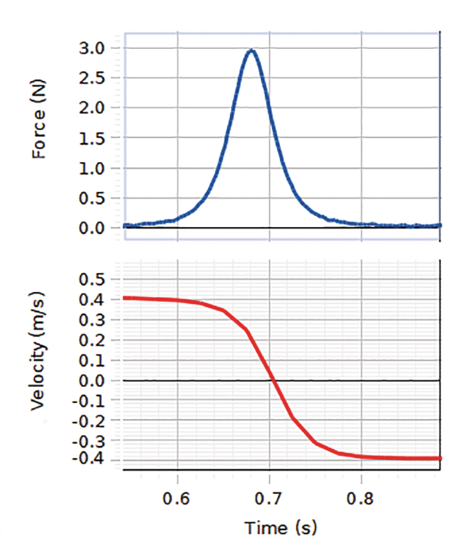
Building Better Barriers
In this investigation, students explore collisions using a PASCO Smart Cart, which records forces during collisions. SPARKvue software is used for data collection and analysis. Students will design their own crash barriers to...
Instantaneous and Average Velocity and Speed
Velocity, speed, and position vs. time are graphed for a Smart Cart moving up and down an inclined track. Software tools are used to find instantaneous velocities and speeds at different moments of the motion, and average velocities...
Acceleration on an Inclined Track
The purpose of this lab is to study the relationships between position, velocity and acceleration for a Smart Cart moving up and then down an inclined track.